How to stop car from burning oil refers to identifying and addressing engine conditions that cause excessive oil consumption. Common causes include worn piston rings, valve seals, PCV valve failure, or using incorrect oil viscosity. Solutions range from switching to the manufacturer-recommended or high-mileage engine oil, repairing faulty components, and ensuring regular oil changes to reduce buildup. Driving habits, such as avoiding constant high RPMs and allowing proper engine warm-up, can also help limit oil burn. Correct diagnosis and maintenance are key to reducing oil consumption and extending engine life.
Table of Contents
What “burning Oil” Really Means
“Burning oil” means engine oil enters the combustion chamber and burns with fuel. This causes blue or gray smoke from the exhaust. It also lowers oil levels, risking engine damage.
How oil gets burned in the engine:
- Worn piston rings let oil pass into cylinders
- Damaged valve seals leak oil into combustion area
- Cracked or worn cylinder walls reduce sealing
- PCV (positive crankcase ventilation) system faults push oil vapor into intake
5 great products that can help reduce oil burning
Liqui Moly Motor Oil Saver helps reduce oil consumption and blue exhaust smoke in worn engines.
Lucas Heavy Duty Oil Stabilizer thickens engine oil to minimize oil burn and reduce wear.
Liqui Moly Viscoplus improves oil viscosity and film strength to limit oil consumption.
Wynn’s Stop Smoke Oil Treatment reduces blue smoke caused by burning engine oil.
Liqui Moly Oil Additive decreases internal engine wear and can help lower oil usage over time.
Engine oil plays a vital rule for your engine. That’s why you should have basic knowledge on engine oil.
Causes Of Oil Burning
The causes of oil burning is key to stopping a car from burning oil. Oil burning happens when engine oil leaks into the combustion chamber and burns along with fuel. This causes blue smoke from the exhaust and lowers oil levels fast. Several engine parts can cause oil burning. Identifying these issues early helps avoid expensive repairs and keeps the engine healthy.
Worn Piston Rings
Worn piston rings are a common cause of oil burning. Piston rings seal the gap between the piston and cylinder wall. They keep oil out of the combustion chamber and maintain compression. Over time, rings wear down or get damaged. This allows oil to pass into the combustion chamber and burn with fuel.
Signs of worn piston rings include:
- Blue smoke from the exhaust during acceleration
- Drop in engine power and efficiency
- Increased oil consumption
- Low compression in affected cylinders
To check piston rings, mechanics perform a compression or leak-down test. Replacing worn rings requires removing the engine head and pistons. This is a labor-intensive repair.
| Symptom | Cause | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Blue exhaust smoke | Oil passing piston rings | Burning oil in combustion |
| Low compression | Ring wear or damage | Poor engine performance |
| High oil use | Oil leaks past rings | More frequent oil refills |
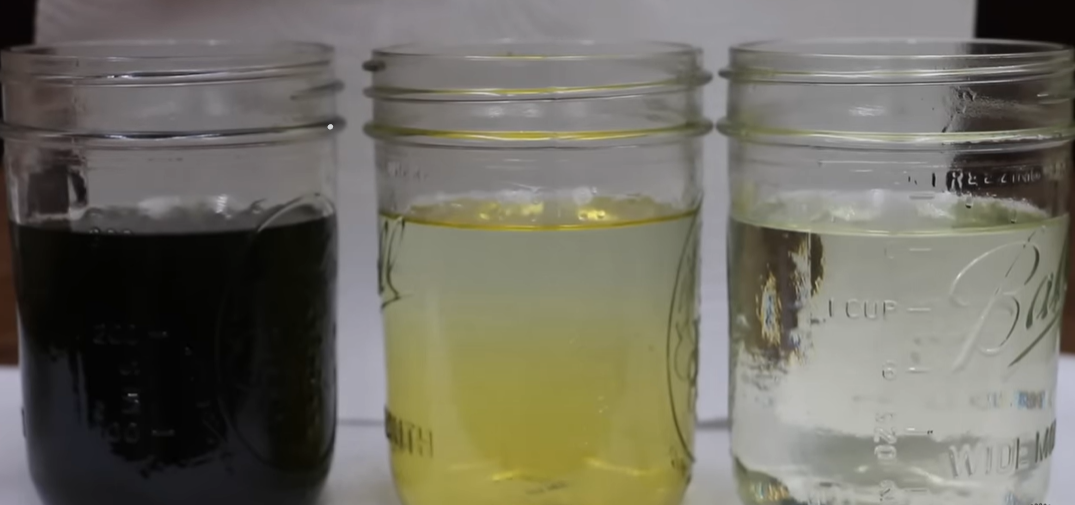
Even some car owners also complain about black engine oil.
Valve Seal Problems
Valve seals prevent oil from leaking into the engine’s cylinders around the valves. These seals wear out due to heat and age. Worn valve seals allow oil to drip into the combustion chamber, causing oil burning.
Common signs of valve seal problems include:
- Blue smoke, especially on startup or idling
- Oil consumption without visible leaks
- Rough engine idle or misfires
Valve seal damage is often worse after the car has been parked for some time. The oil seeps past the seals and burns when the engine starts. Repairing valve seals involves removing the cylinder head and replacing the seals. This can be a moderate to complex job depending on the engine design.
If you see your engine oil smell like gasoline you should take it seriously!
Pcv Valve Issues
The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve controls gases inside the engine crankcase. A faulty PCV valve can cause pressure buildup and force oil into the intake manifold. This oil then burns in the engine, causing blue smoke and oil consumption.
Signs of PCV valve problems include:
- Rough idle and engine stalling
- Increased oil consumption
- Oil leaks and sludge buildup
- Blue exhaust smoke
PCV valves are usually small and inexpensive. Checking and replacing a faulty PCV valve is simple and can reduce oil burning. Regular maintenance of the PCV system helps keep oil in place and the engine clean.
Cylinder Wall Damage
Cylinder wall damage occurs when the smooth surface inside the cylinder wears or scratches. This damage harms the seal between the piston rings and cylinder wall. Oil can then leak past the rings into the combustion chamber and burn.
Causes of cylinder wall damage include:
- Poor lubrication
- Overheating
- Foreign particles in the engine
- Corrosion from moisture
Symptoms of cylinder wall damage are:
- Blue smoke from the exhaust
- Loss of engine power
- Increased oil consumption
- Knocking or unusual engine noise
Repairing cylinder walls may involve boring and honing the cylinders or replacing the engine block in severe cases. Maintaining proper oil levels and quality prevents damage to the cylinder walls.
Signs Of Excessive Oil Burning
Excessive oil burning in a car can cause serious engine problems. Knowing the signs of oil burning helps prevent costly repairs. Oil burning happens when oil leaks into the engine’s combustion chamber and burns along with fuel. This leads to damage and poor engine health.
Blue Smoke From Exhaust
Blue smoke coming from the exhaust pipe is a clear sign of oil burning. This happens because oil is burning inside the engine. The smoke usually has a distinct blue or grayish-blue color. You might notice the smoke most during:
- Starting the engine
- Accelerating
- Idling
Blue smoke means oil is slipping past seals or worn piston rings into the combustion chamber. This problem needs quick attention to avoid engine damage.
Common causes of blue smoke include:
- Worn valve seals
- Damaged piston rings
- Broken turbocharger seals
- Clogged PCV valve
Ignoring blue smoke can lead to:
- Engine overheating
- Loss of power
- High repair costs
| Cause | Effect | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Worn Valve Seals | Oil leaks into combustion chamber | Replace seals |
| Damaged Piston Rings | Oil burns during combustion | Engine rebuild or ring replacement |
| Clogged PCV Valve | Pressure build-up causes leaks | Clean or replace PCV valve |
Low Oil Levels
Low oil levels often signal excessive oil burning. Check oil level regularly using the dipstick. If the oil level drops quickly without leaks, oil is likely burning inside.
Signs of low oil levels include:
- Warning lights on the dashboard
- Engine noise or knocking sounds
- Overheating engine
Driving with low oil can cause severe engine damage. Oil lubricates the engine parts and prevents wear. Burning oil means less lubrication, which leads to friction and heat.
Here are steps to monitor and maintain oil levels:
- Check oil level every 1,000 miles or monthly
- Top up with the correct oil type if low
- Inspect for external leaks
- Schedule engine check if oil drops fast
Engine Misfires
Oil burning can cause engine misfires. Misfires happen when the fuel-air mixture in the cylinder does not ignite properly. Oil in the combustion chamber disrupts this process.
Symptoms of misfires include:
- Rough idling
- Loss of power
- Engine shaking
- Poor fuel economy
Oil fouling on spark plugs is a common cause. The oil coats the spark plugs, stopping them from firing correctly. This creates incomplete combustion and misfires.
Fixing engine misfires caused by oil burning involves:
- Replacing spark plugs
- Checking valve seals and piston rings
- Cleaning or replacing the PCV valve
Decreased Performance
Oil burning reduces engine performance. The engine loses power and runs less smoothly. You may feel the car is slower or struggles during acceleration.
Reasons for decreased performance from oil burning:
- Oil fouling on spark plugs
- Reduced compression due to worn piston rings
- Dirty air-fuel mixture from burning oil
Common effects of poor performance are:
- Lower fuel efficiency
- Hard starting
- Engine hesitation
Maintaining engine health improves performance. Regular oil changes and prompt repairs keep the engine running well. Detect signs early to avoid permanent damage.
How To Stop Car From Burning Oil (actionable Fixes)
Cars that burn oil waste fuel and can harm the engine over time. Understanding how to stop your car from burning oil helps save money and keep the vehicle running smoothly. This section provides actionable fixes to reduce oil burning and extend engine life. Follow these tips to protect your car and avoid costly repairs.
Checking Pcv Valve
The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve controls gases inside the engine. A faulty PCV valve causes pressure build-up, pushing oil into the combustion chamber. This leads to oil burning and smoke from the exhaust.
Steps to check the PCV valve:
- Locate the PCV valve on the valve cover or intake manifold.
- Remove it carefully and shake it.
- If it rattles, it is usually good; if not, it needs replacement.
- Inspect for clogging or damage.
Replacing the PCV valve is cheap and easy but prevents major engine problems. Keep it clean to allow proper ventilation.
| Signs of Bad PCV Valve | Effects on Engine |
|---|---|
| Rough idle or stalling | Oil leaks and increased oil consumption |
| Blue smoke from exhaust | Engine misfires or decreased performance |
| Oil in air filter or hoses | Excessive pressure inside crankcase |
Regular Oil Changes
Changing oil regularly is crucial to reduce oil burning. Old oil loses its ability to lubricate engine parts well. Dirty oil can cause sludge build-up, which damages seals and piston rings.
Follow these tips:
- Change oil every 3,000 to 5,000 miles or as the manufacturer recommends.
- Use the right oil grade for your car.
- Check oil level monthly.
- Replace the oil filter with every oil change.
Regular oil changes help keep engine parts clean and running smoothly. This reduces friction and stops oil from leaking into the combustion chamber.
Using Quality Oil
Quality oil lasts longer and protects your engine better. Low-quality oil breaks down fast and burns more easily. Choose oils that meet industry standards and suit your car’s engine type.
Look for these oil types:
- Synthetic oil: Better resistance to heat and breakdown.
- Semi-synthetic oil: Good balance of cost and protection.
- High mileage oil: Designed for older engines to reduce leaks.
Using quality oil reduces oil burning and keeps your engine clean. It also helps improve fuel efficiency and engine power.
Avoid Overfilling
Too much oil in the engine causes excess pressure and leads to oil burning. Overfilling can damage engine seals and cause leaks. It also makes the oil foam, reducing lubrication.
How to avoid overfilling:
- Check oil level with the dipstick after filling.
- Fill oil slowly and stop at the recommended level.
- Refer to your owner’s manual for correct oil quantity.
- Have a mechanic drain excess oil if overfilled.
Keep oil at the correct level to protect your engine and prevent burning.
Use Correct Oil & Filter
Using the right oil and filter helps reduce oil burning. Oil viscosity affects engine performance and wear. A wrong filter may not clean oil properly, allowing dirt to damage engine parts.
Tips for choosing oil and filter:
- Follow manufacturer’s recommendations for oil grade and type.
- Buy filters that match your car model and brand.
- Replace oil filter at every oil change.
- Check for high-quality brands with good reviews.
Correct oil and filters keep the engine clean and reduce oil consumption.
Try Oil Additives
Oil additives improve oil performance and reduce oil burning. Some additives thicken oil to seal leaks, while others clean engine parts. Choose additives that suit your car’s needs.
Common types of oil additives:
- Seal conditioners: Help swell and restore seals.
- Detergents: Clean sludge and deposits.
- Viscosity improvers: Maintain oil thickness at high temperatures.
Use additives sparingly and follow product instructions. Additives can extend engine life and reduce oil consumption when used properly.
Add Fuel System Cleaner
Fuel system cleaners remove carbon deposits inside the engine. Carbon buildup causes piston rings to stick, increasing oil burning. Cleaning the fuel system helps improve engine compression and reduce oil leaks.
Steps to use fuel system cleaner:
- Buy a reputable fuel system cleaner suitable for your car.
- Pour the cleaner into the fuel tank before refueling.
- Run the engine for several miles to allow cleaner to work.
- Repeat every few thousand miles as preventive maintenance.
Fuel system cleaners improve engine efficiency and lower oil consumption.
Routine Engine Inspections
Regular engine inspections catch oil burning problems early. A mechanic can spot worn piston rings, valve seals, or other causes. Early detection saves repair costs and prevents engine failure.
Inspection checklist:
- Check for oil leaks around the engine.
- Inspect spark plugs for oil fouling.
- Test compression to check piston ring condition.
- Examine exhaust smoke color and amount.
- Listen for unusual engine noises.
Routine inspections keep your car in good shape and reduce oil burning risks.
Diy Fixes To Reduce Oil Burning
Excessive oil burning can harm your engine and cause costly repairs. Many car owners want to fix this problem themselves. DIY fixes to reduce oil burning save money and keep the engine healthy. Some simple steps help lower oil consumption and improve engine performance. This guide explains easy repairs anyone can do with basic tools.
Replacing Valve Seals
Valve seals keep oil from leaking into the engine’s combustion chamber. Worn or damaged valve seals cause oil to burn and smoke from the exhaust. Replacing them can stop oil burning and improve engine life.
Steps to replace valve seals:
- Remove the valve cover to access the valve train.
- Use a valve spring compressor tool to compress springs and remove old seals.
- Install new valve seals carefully to avoid damage.
- Reassemble the valve cover and other parts.
Signs that valve seals need replacement:
- Blue smoke from the exhaust, especially on startup.
- Oil consumption higher than normal.
- Rough engine idle or poor performance.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Valve Spring Compressor | Compress valve springs to remove old seals |
| Socket Wrench Set | Remove valve cover bolts |
| New Valve Seals | Replace worn seals to stop oil leakage |
Replacing valve seals takes time but is a cost-effective way to reduce oil burning. Follow safety instructions and engine manual for best results.
Cleaning Or Replacing Pcv Valve
The PCV (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) valve controls pressure inside the engine. A clogged or broken PCV valve causes oil burning by raising crankcase pressure. Cleaning or replacing it restores proper ventilation and reduces oil loss.
How to check and fix the PCV valve:
- Locate the PCV valve on the valve cover or intake manifold.
- Remove the valve and inspect it for dirt or blockage.
- Shake the valve; a rattling sound means it still works.
- Clean it using a carburetor cleaner or replace it if damaged.
- Reinstall the valve and check for leaks.
Benefits of a working PCV valve:
- Reduces oil consumption by controlling crankcase pressure.
- Improves engine efficiency and lowers emissions.
- Prevents sludge buildup inside the engine.
| PCV Valve Status | Effect on Engine |
|---|---|
| Clean and functional | Normal oil use and pressure |
| Clogged or broken | Increased oil burning and pressure |
Replacing the PCV valve is an easy, low-cost fix that can reduce oil burning significantly. Regular checks keep the engine running smoothly.
Using Oil Additives
Oil additives improve the quality and performance of engine oil. Certain additives help reduce oil burning by sealing small leaks and improving oil viscosity. They are simple to use and can extend engine life.
Common types of oil additives for burning oil:
- Seal conditioners: Swell and soften worn seals to stop leaks.
- Viscosity improvers: Maintain oil thickness at high temperatures.
- Anti-wear agents: Protect engine parts from damage and wear.
How to use oil additives:
- Choose an additive suitable for your engine type and oil.
- Pour the recommended amount into the engine oil filler cap.
- Run the engine for several minutes to circulate the additive.
- Monitor oil consumption and engine performance.
| Additive Type | Main Benefit |
|---|---|
| Seal Conditioners | Reduce oil leaks from seals and gaskets |
| Viscosity Improvers | Keep oil thick to reduce burning |
| Anti-Wear Agents | Protect engine parts from wear |
Note: Oil additives do not fix severe engine damage. They work best for minor leaks and early signs of oil burning.
When To Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to seek professional help is crucial for stopping your car from burning oil. Some oil burning problems need simple fixes. Others require expert attention to avoid serious engine damage. Acting fast saves money and keeps your car running safely. Watch for signs like thick blue smoke, frequent oil top-ups, and engine misfires. These often mean the problem is beyond home repair. A professional mechanic can diagnose issues using special tools and tests. This section explains key situations requiring expert help to stop your car from burning oil.
Engine Overhaul Needs
An engine overhaul may be necessary when oil burning is severe and ongoing. This is a major repair where the engine is taken apart, cleaned, and rebuilt. Overhauls fix worn or damaged parts causing oil leaks and burning.
Signs you might need an engine overhaul:
- Excessive blue smoke from the exhaust
- Loss of engine power and poor fuel economy
- Frequent oil consumption despite topping up
- Knocking or unusual engine noises
- Low oil pressure warning light
The overhaul process includes:
- Removing the engine from the car
- Disassembling the engine block and components
- Cleaning and inspecting all parts
- Replacing damaged parts like bearings, seals, and gaskets
- Reassembling and testing the engine
This repair restores engine health and stops oil burning effectively. It is costly and time-consuming but often the only solution for old or heavily damaged engines.
Piston Ring Replacement
Piston rings seal the gap between the piston and cylinder walls. Worn or broken rings let oil enter the combustion chamber, causing oil burning. Replacing piston rings is a common fix for oil burning.
Symptoms of bad piston rings:
- Blue exhaust smoke, especially during acceleration
- Loss of compression and engine power
- Increased oil consumption
- Rough idling or misfires
Replacing piston rings involves:
- Removing the engine head and pistons
- Cleaning piston grooves
- Installing new piston rings carefully
- Reassembling engine parts and checking seals
This repair improves engine compression and reduces oil burning. It requires skill and tools, so professional help is recommended.
Cylinder Repair Options
Damaged cylinder walls cause oil to leak past pistons and burn. Scratches, scoring, or wear inside cylinders worsen oil burning. Cylinder repairs restore proper sealing and engine function.
Common cylinder repair methods:
| Repair Type | Description | When Used |
|---|---|---|
| Honing | Smooths minor scratches and restores cylinder surface | Light wear and scratches |
| Boring | Enlarges cylinder to remove deep damage, requires oversized pistons | Severe cylinder damage |
| Sleeving | Inserts a new cylinder liner into the block | Extensive wear or cracks |
Each option requires disassembly and precise work. Choose based on damage severity and cost. A mechanic can inspect cylinders and recommend the best fix.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can I Tell If My Car Is Burning Oil?
Check for blue smoke from the exhaust and frequent oil top-ups. Also, notice engine performance drops or oil smell inside the cabin.
What Causes A Car To Burn Oil Excessively?
Worn piston rings, valve seals, or damaged gaskets cause oil to leak into combustion chambers. Poor maintenance worsens the issue.
Can Using Synthetic Oil Reduce Oil Burning?
Yes, synthetic oil resists breakdown better and lubricates engine parts more efficiently, reducing oil consumption and burning.
How Often Should I Check My Car’s Oil Level?
Check oil at least once a month and before long trips to spot issues early and prevent engine damage.
Conclusion
Stopping your car from burning oil protects the engine and saves money. Check oil levels often and change oil on time. Use the right oil type for your car model. Fix leaks and worn-out parts quickly to avoid damage. Clean or replace air filters regularly for better engine health.
Small steps can prevent big car problems. Take care of your vehicle to keep it running smoothly. Simple habits help your car last longer and perform well. Stay attentive and keep your engine healthy every day.



2 Replies to “How to Stop Car from Burning Oil (2026) – Causes, Repairs & Best Solutions”
Comments are closed.